Compile your project first if it is complex to compile
Compile your project as normal but add this flag to get better debugging infomation -gcflags="-N -l".
use flag attach or exec to run your program first before running the debugger.
Visual studio Code Remote Debugging
Orignal infomation from this webite
Do not use this flag as vscode go plugin does not surport version 2 yet.
--api-version=2
To remote debug using VS Code, you must first run a headless Delve server on the target machine. To do this open a terminal and type in below example in your project folder to compile and debug your project.
dlv flags which can be changed.
debug flag means compile and begin debugging main package in current directory, or the package specified. usage
$ dlv debug --headless --listen=:2345 --log
exec <path/to/binary> flag means execute a precompiled binary, and begin a debug session. usage
$ dlv exec /tmp/test/testfile --headless --listen=:2345 --log
attach pid <pid number> attach to running process pid number and begin debugging. usage
Get pid number of the program running.
$ pgrep programName
$ dlv attach 1234 --headless --listen=:2345 --log
Any arguments that you want to pass to the program you are debugging must be passed to this Delve server that runs on the target machine
For example:
$ dlv debug --headless --listen=:2345 --log -- -myArg=123
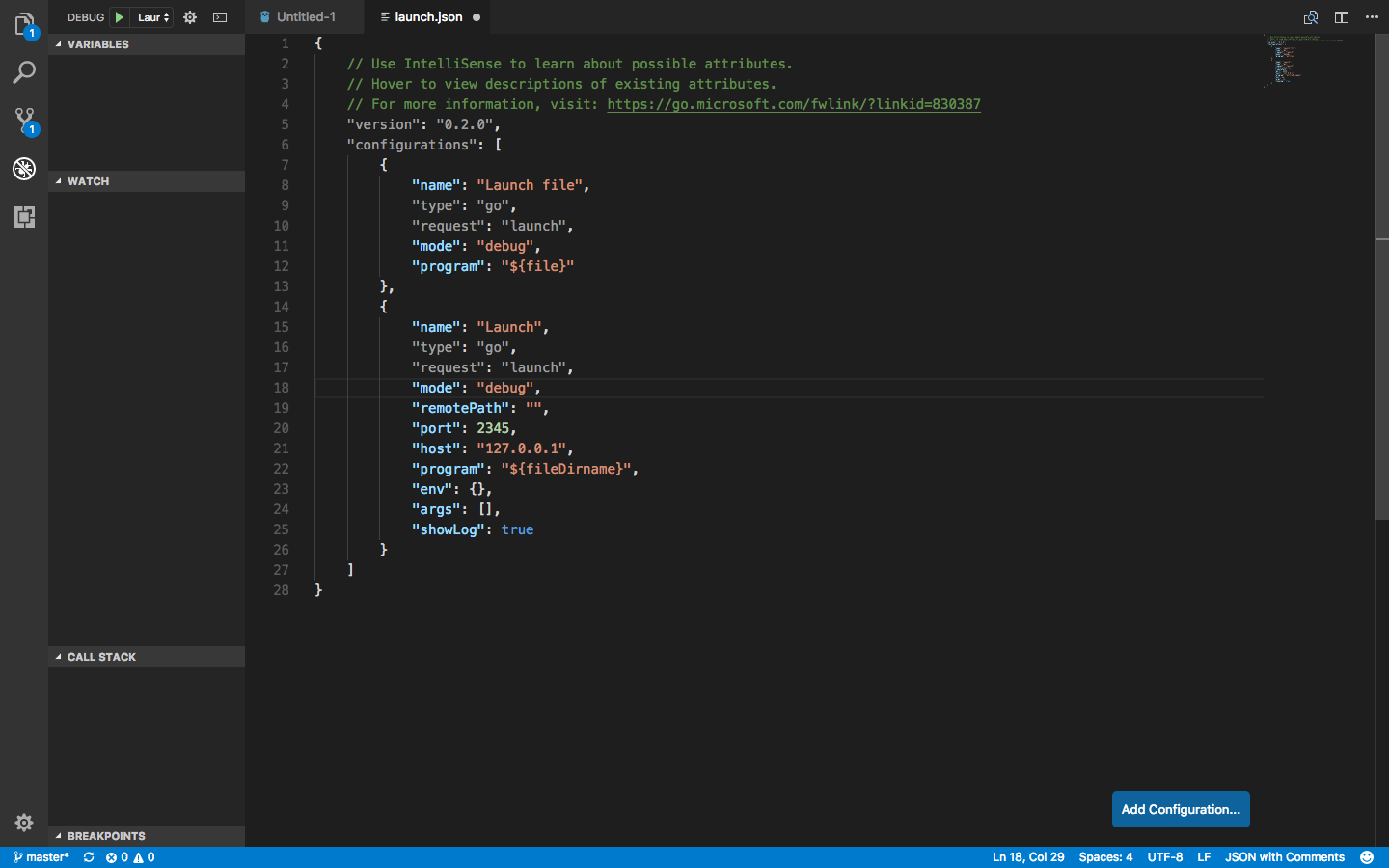
Then, create a remote debug configuration in VS Code launch.json.
{
"name": "Remote",
"type": "go",
"request": "launch",
"mode": "remote",
"remotePath": "${workspaceRoot}",
"port": 2345,
"host": "127.0.0.1",
"program": "${workspaceRoot}",
"env": {}
}
When you launch the debugger with this new Remote target selected, VS Code will send debugging commands to the dlv server you started previously instead of launching it’s own dlv instance against your app. The above example runs both the headless dlv server and the VS Code debugger locally on the same machine.